Electronic Dynamic Bias Systems
Cathode Bias Operation
Over the years I noticed people being overly fussy about having a certain value resistor for R1 in the circuit below. Allegedly resistor R1 is needed to "prevent the cathode from soaring to B+ voltage" or "establishing cut-off bias". Both claims are generally not true. Let's look at a working example:
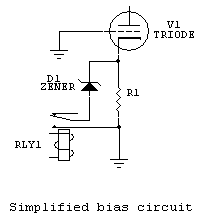
V1=3CX1200A7 (used for measurement data in this example)
R1 is cathode bias resistor when relay is open
D1 is normal zener diode
This is a simplified bias circuit, but it does electrically represent the function of this system.
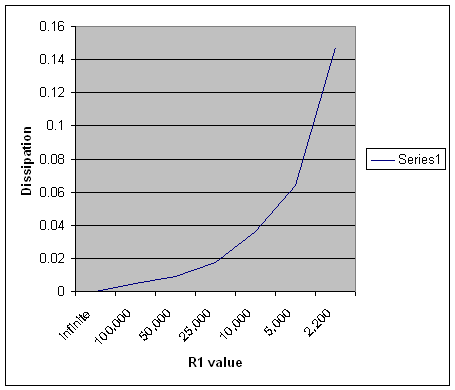
| R1 | Bias | R1 Pd | Ip Amperes |
| infinite | 24 | 0 | 0 |
| 100,000 | 21.3 | 0.0045369 | 0.000213 |
| 50,000 | 21 | 0.00882 | 0.00042 |
| 25,000 | 20.75 | 0.0172225 | 0.00083 |
| 10,000 | 19 | 0.0361 | 0.0019 |
| 5,000 | 17.9 | 0.064082 | 0.00358 |
| 2,200 | 18.018 | 0.14756742 | 0.00819 |
| 3CX1200A7 | 3650 volts anode | ||
Table to the left is dissipation in watts for various values of R1 resistance. Note dissipation increases as resistance decreases over this range. At some point R1 dissipation will peak and start to decline as resistance goes below that value, but this would be with grossly excessive standby current.
Over a normal range of R1 values, dissipation is insignificant.
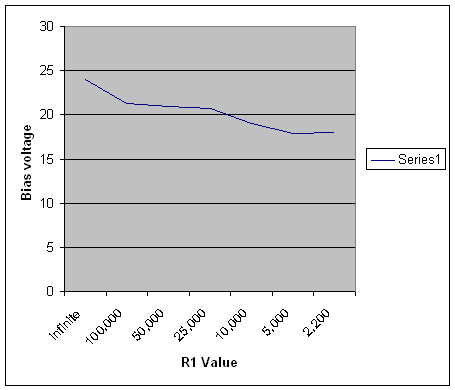
| R1 | Bias | R1 Pd | Ip Amperes |
| infinite | 24 | 0 | 0 |
| 100,000 | 21.3 | 0.0045369 | 0.000213 |
| 50,000 | 21 | 0.00882 | 0.00042 |
| 25,000 | 20.75 | 0.0172225 | 0.00083 |
| 10,000 | 19 | 0.0361 | 0.0019 |
| 5,000 | 17.9 | 0.064082 | 0.00358 |
| 2,200 | 18.018 | 0.14756742 | 0.00819 |
| 3CX1200A7 | 3650 volts anode | ||
Table to the left indicates measured cathode voltage with various values of R1 resistance. Note that a completely open circuit only produces ~24 volts cathode bias on the 3cx1200A7 tube! A typical 3-500Z produces about 30-35 volts cathode bias with no resistor.
Note there is very little change in bias voltage over the range of 2000 ohms to infinity! The cathode is an almost perfect constant voltage source at low currents.